Abstract
Users of Websense Data Security that are reviewing DLP incidents can be attacked via Cross-Site Scripting. This issue can be exploited using a specially crafted email, or by sending a specially crafted HTTP request through the Websense proxy. The attacker-supplied code can perform a wide variety of attacks, such as stealing session tokens, login credentials, performing arbitrary actions as victims, or logging victims' keystrokes.
Tested versions
This issue was discovered on Websense Triton v7.8.3 and Websense appliance modules V-Series v7.7. Other versions may be affected as well.
Fix
This issue is resolved in TRITON APX Version 8.0. More information about the fixed can be found at the following location: https://support.forcepoint.com/KBArticle?id=Vulnerabilities-resolved-in-TRITON-APX-Version-8-0
Introduction
Websense Data Security Suite contains three modules - Data Security Gateway, Data Discover, and Data Endpoint - that can help manage the risk of losing your data to malicious users or accidental misuse.
Email Security Gateway monitors the flow of email messages in real time, and has a Message Log where you can view records of inbound messages. The messages include client details such as sender address. All input from the (mail) client is not properly encoded when presented on the screen, resulting in Cross-Site Scripting.
A remote attacker can use this issue to inject malicious JavaScript code into the output of the application, which will execute within the browser of any authenticated user (admin or auditor) who views the relevant DLP incident. The attacker-supplied code can perform a wide variety of actions, such as stealing victims' session tokens or login credentials, performing arbitrary actions on their behalf, or logging their keystrokes.
Details
This issue can be exploit via any part of an email message that is shown in the Message Log. In the screenshots below, a malicious user or external attacker has sends an email with the 'Sender address' containing Cross-Site Scripting payload. When a Triton user (victim) views the malicious log entry of the specially crafted email - both inbound and outbound messages - the payload will be executed in the victim's browser.
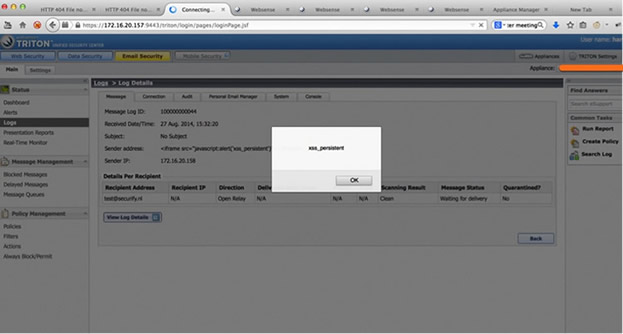 Figure 1: Cross-Site Scripting in Audit Log entry of Websense Email Security
Figure 1: Cross-Site Scripting in Audit Log entry of Websense Email Security
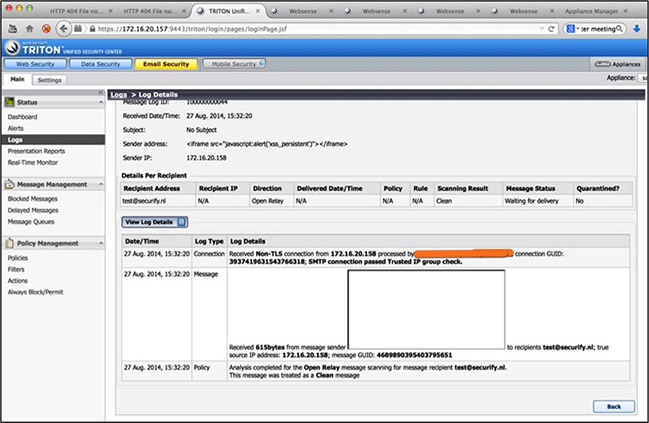 Figure 2: Message log type details (
Figure 2: Message log type details (<IFRAME>) shows that client data is displayed on screen in an insecure way